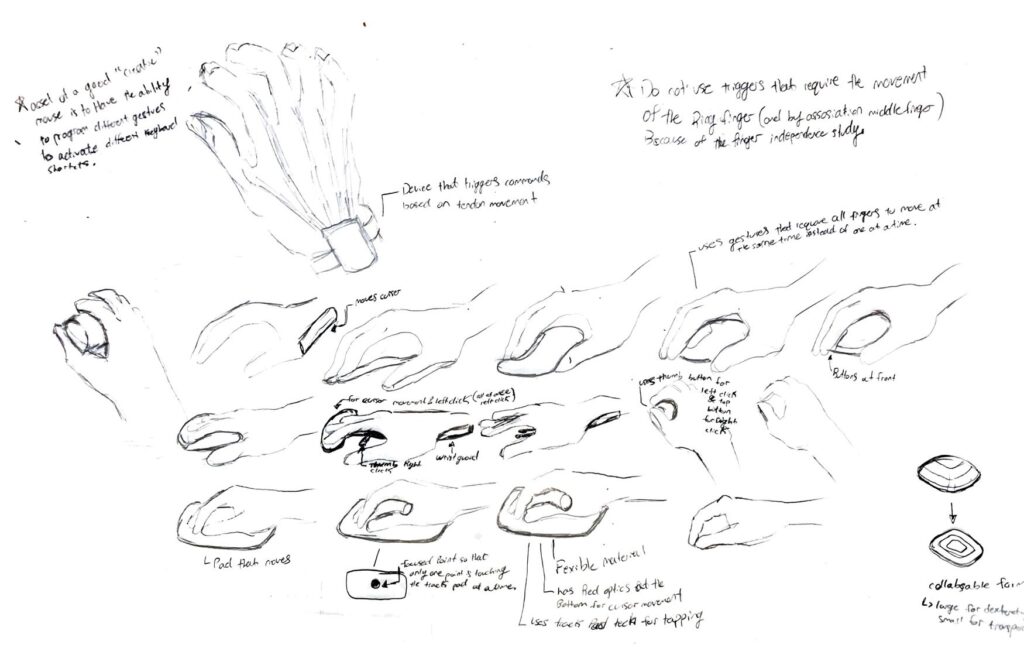

Computer Mouse Redesign

jumping off of what I learned from tendon strength and hand position effort , I felt it could be insightful to learn about people who have conditions where their tendon strength has been injured.
Neuropathy is damage or dysfunction of one or more nerves that typically results in numbness, tingling, muscle weakness and pain in the affected area. Neuropathies frequently start in your hands and feet, but other parts of your body can be affected too.
-carpal tunnel is a type of hand neuropathy
-Hand Neuropathy can negatively effect hand manual dexterity (the ability to use your hands in a skillful, coordinated way to grasp and manipulate objects and demonstrate small, precise movements).
Indoor Rock climbing may provide some insight into what kinds of shapes and forms are easier to grip (requiring less hand dexterity and grip strength)
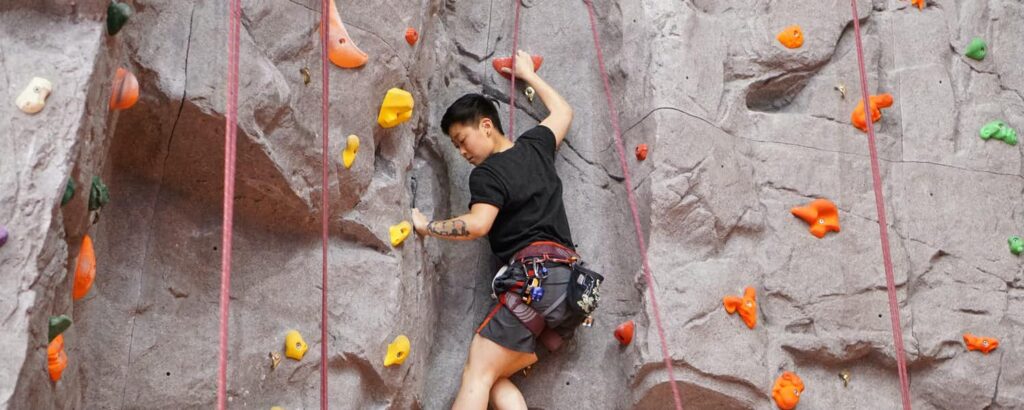


there are many types of rock climbing hold including horns, jugs, flakes, underclings, pockets, slopers, pinches, crimps, and ledges. However the easiest of these holds are Jugs.
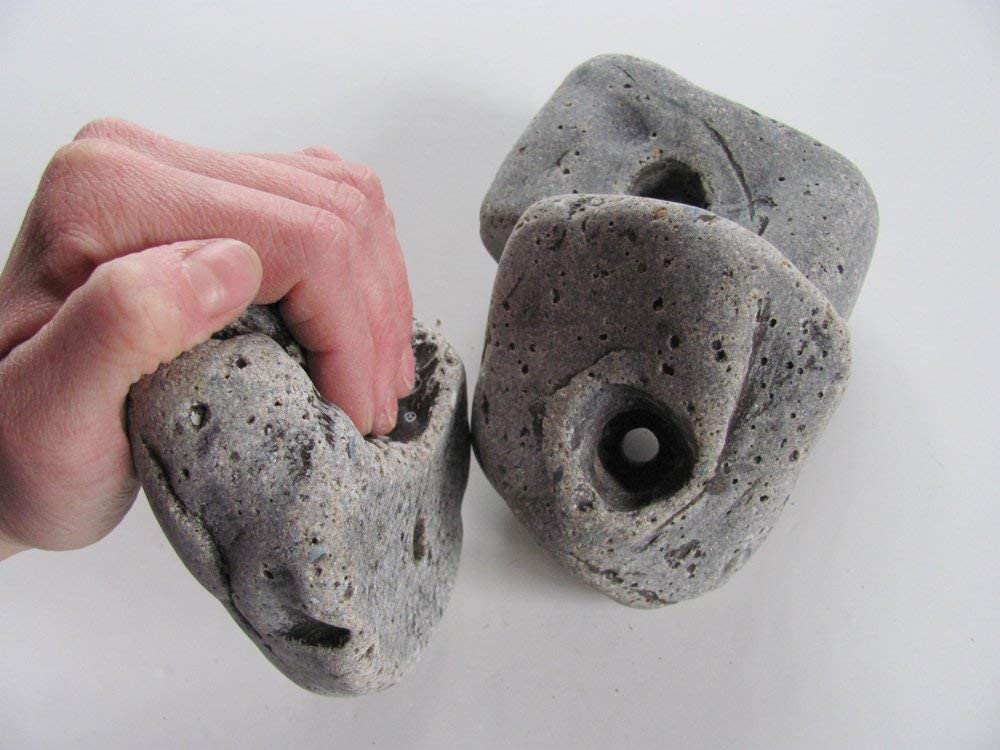

Normally smaller holds are considered harder and thus because of their large size, Horns can also be considered to be easier than most holds, but because they are so big (bigger than the size of your hand), it can be difficult to maintain this grip for a long time.

This is why Jugs are the easiest hold; small enough to fit nicely for the size of an average hand, yet large enough to require little grip strength.
SOURCES
C. (2019). Neuropathy (Peripheral Neuropathy). Retrieved November 28, 2020, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14737-neuropathy
A. (2015). THE IMPORTANCE OF MANUAL DEXTERITY. Retrieved November 28, 2020, from https://www.adea.org/GoDental/Application_Prep/Preparing_for_Dental_School/The_Importance_of_Manual_Dexterity.aspx
R. (2018). How to Use Rock Climbing Holds. Retrieved November 28, 2020, from https://www.rei.com/learn/expert-advice/climbing-holds.html

Overarching problem to solve is fatigue (especially because in the context of the creative industry, users spend long hours with the mouse, therefore allowing them to comfortably use the mouse for as long as possible is the number one challenge to solve. it seems fatigue while using computers is usually caused by:
Finger tendon gliding exercises are used in physiotherapy to rehabilitate an injured ligaments, muscles or tendons in the hand or wrist. These exercises include transitioning your hand between specific hand positions including the:
relaxed, straight, duck, hook, flat fist, and full fist, and tabletop positions.
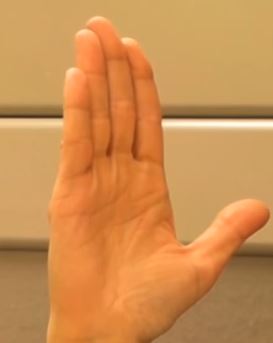




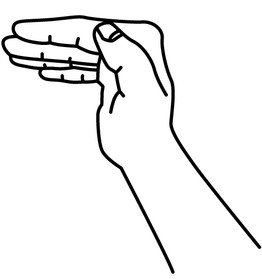
This is important because all of these positions are used by physiotherapists because they activate the hand tendons and require a level of strength from your forearm muscles to be able to do these movements properly.
These positions require effort to hold therefore these are great for training your hand back into working condition, but I should stay away from designing any concept or form that requires the user to make any of these positions.
SOURCES
S. (2015, July 29). Tendon Gliding – Southlake Hand Therapy. Retrieved November 27, 2020, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dUhjUBAQv30

Air hockey uses air to blow up through the table via tiny holes to allow the puck to glide easier across the table simulating ice.

what if this was used in the mouse itself to allow a more free and loose movement experience
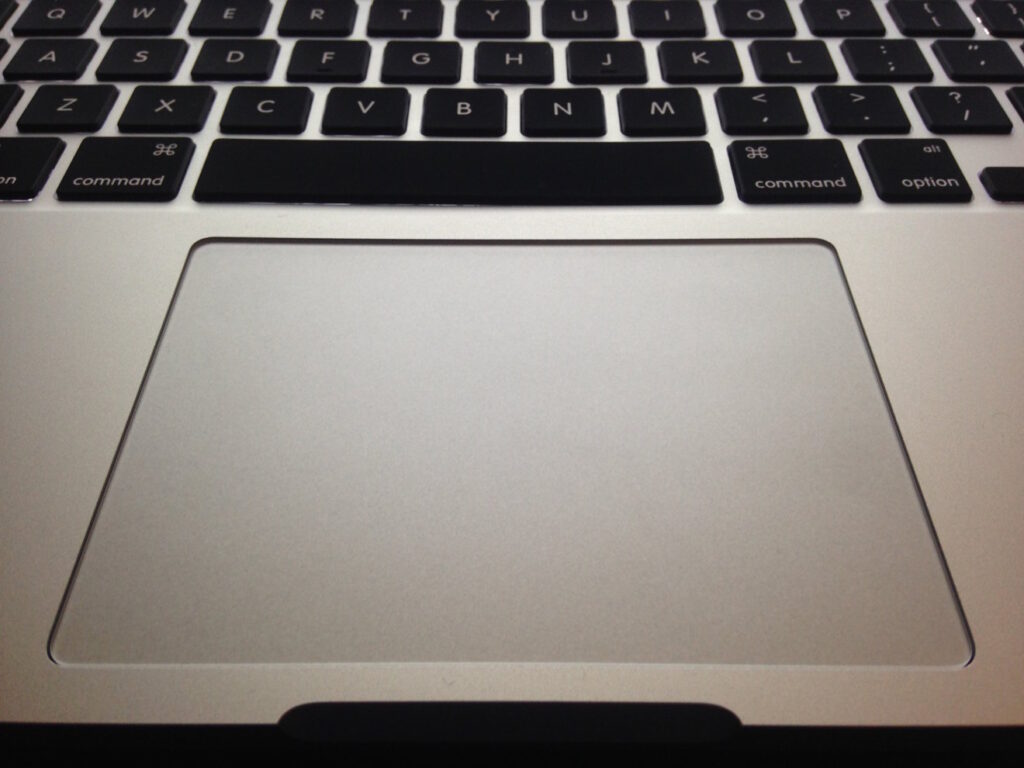

track pads are actually a very interesting concept and have much promise. They allow you to move the cursor with something very low profile, and most newer versions allows users to left and right click simply by tapping the pad rather than pressing an actual button (would require more force). The issue is that users need to put their hand and fingers into tabletop, or hook type of position for use; and as I found in this article here, those positions are to be avoided.
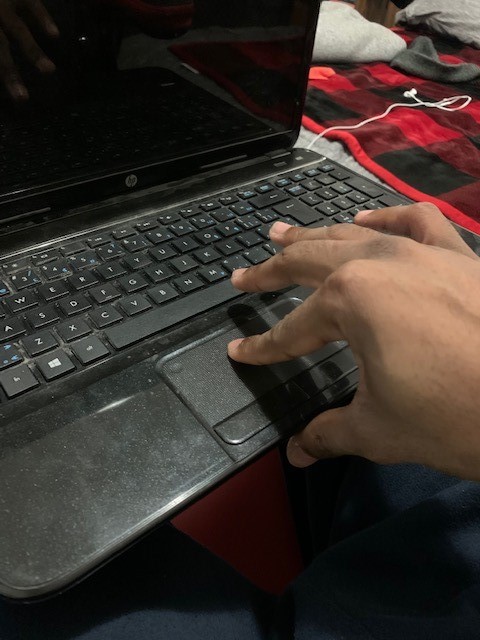
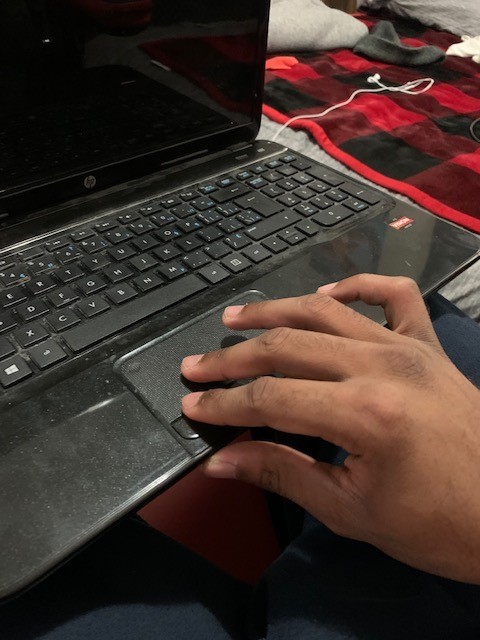
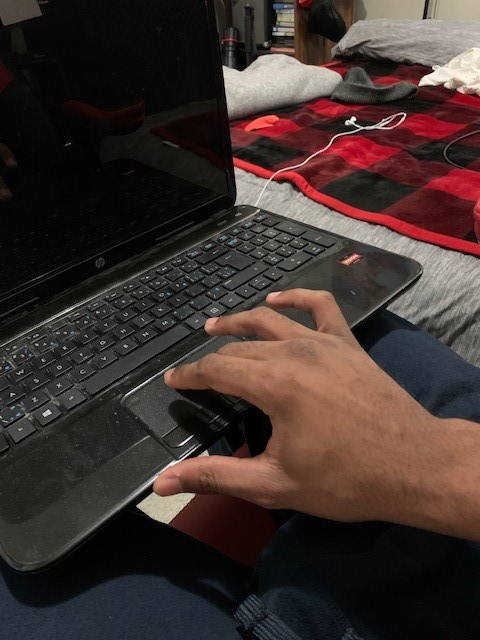




[Insight: what if there was a way of using track pad technology in a design that allowed users’ hands to be in a neutral position. What if we could use a track pad by moving our entire hand rather than isolating a couple fingers (as found here, isolating fingers can also lead to fatigue).
A study posted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information and published by the Europe PMC founders group investigates natural movements of the right hand in day to day activity. The results were as follows:
-The thumb is the most independent digit, the pointer finger is the most independent finger (meaning it is easiest to move that finger by itself without strain), and the ring finger is the least independent of all (meaning it is difficult to isolate that finger).
-it is always harder to move a finger independently from a directly adjacent finger than it is to move a finger independently from one that is farther away.
[insight: since it is more difficult to move certain fingers by themselves, if i make a design that requires the frequent use of an isolated finger (especially the ring and middle fingers), it will be likely to lead to hand fatigue]
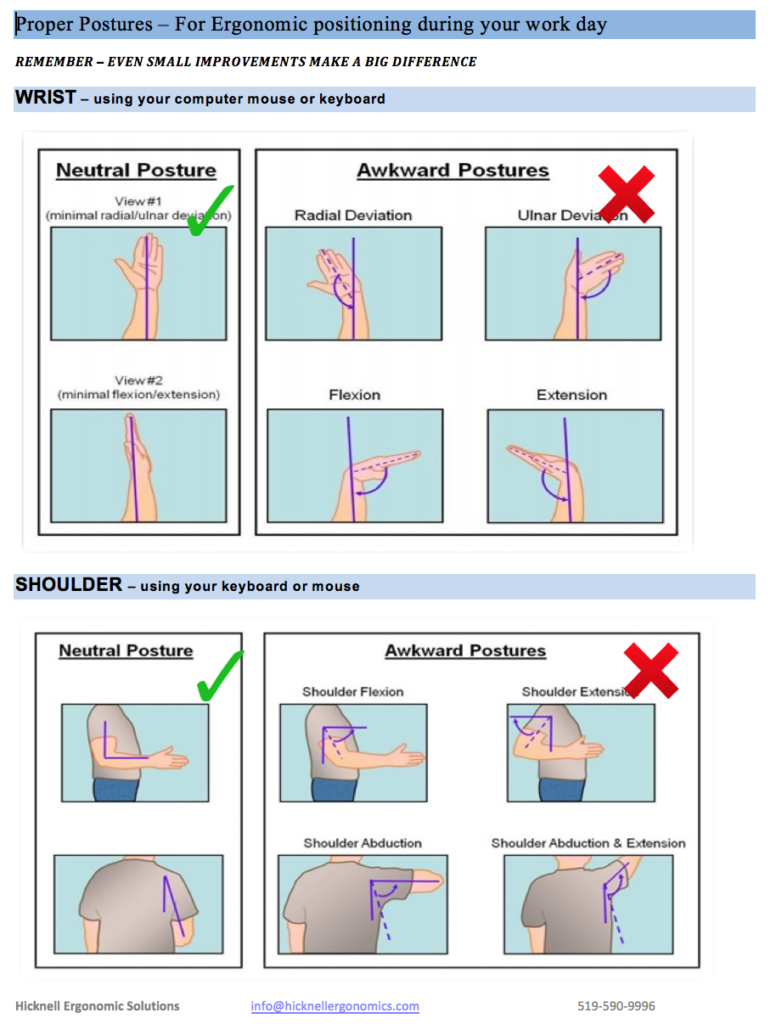
-IDEA: what if i designed a stationary form that used direction force to move the cursor instead of designs that use the movement of fingers to do so. using pressure sensors to dictate the speed of the cursor and programming in a way where the force required to move the cursor is small enough to be usable for long periods, while being large enough to prevent accidental or unwanted movements.
IDEA: what if i created a mouse that could rotate to a neutral position for both hands.
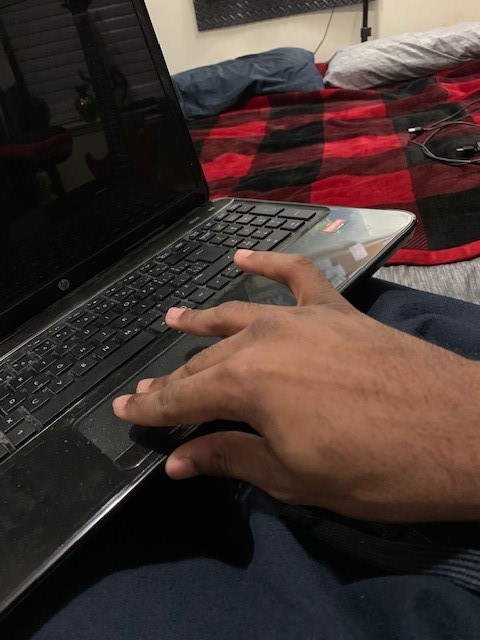
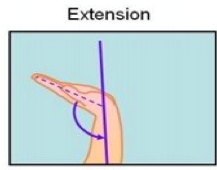
[IMPORTANT INSIGHT: I should then also stay away from designing a form that causes one or two fingers to rest in different positions than the others (the resting position of all fingers should be the same). For example

this picture shows how the resting position of the index and middle fingers are at different heights from the ring and pinky. ]
– Steve Meagher a physiotherapist specializing in ergonomics says that the ulnar nerve and the median nerve both tend to get pinched when your wrist is sat on the edge of a desk while utilizing a mouse. further more, when you physically move the mouse around, you are rubbing and grinding into those two nerves which can cause much discomfort.
(solution is to either position the wrist and arm in a way that is not sitting directly on the base of the wrist, or to provide extra cushioning to decrease the immediate hardness of the desk being used. )
he also says that those particular nerves become aggravated when your wrist is in the extended position for long periods of time)
SOURCES
Ingram, J., Körding,, K., Howard, I., & Wolpert, D. (n.d.). The statistics of natural hand movements. Europe PMC Founders Group.
Meagher, S. (2016, November 10). Gaming- Mouse Position and Wrist Pain. Retrieved November 26, 2020, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xS7EzEKScs
I made a research presentation communication piece to my audience in order to gain some feedback on my design possibilities. this site is https://w1w1w1w1.wixsite.com/website-2
I then downloaded the feedback form onto my computer to analysis the results.
Some of the most repeated things were:
small, cheap, long hours, comfort, function
Some of the main points that persisted were that:
1) there may be a market for a hybrid of efficiency, comfort and functionality instead of improving only one
2)small, cheap, and wireless were among the most important features when looking for a mouse
3) hand size was pointed out as important
4)shallow mice are not good for long hours
[interesting insight is that a lot of people mentioned comfort as one if the top things they look for in a mouse, yet they value the efficiency and functionality as possibilities for this project. – maybe this mean that comfort is just a design requirement but doesn’t need to be necessarily improved. ]
This feedback is prompting me to possibly find a hybrid between some aspects of my design possibilities.
Within the work force, many workers are affected by RSIs
I wanted to find some more specifi information about the impact of wrist injuries in the labour fource.
aproximately ” 1. 1.8 million workers are afflicted by RSI’s per year: Almost 2 million US workers suffer from RSI’s like carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) and tendinitis each year. [1] 600,000 workers take time off work each year to recuperate and treat their RSI. “
“ 1 in every 50 workers has RSI symptoms: According to the Trades Union Congress (TUC), 1 in every 50 workers has reported experiencing RSI symptoms. [3] These numbers are even higher in industries like computer operation where the prevalence is as high as 1 in every 4 employees.”
Approximately 50% of people ” who work with computers suffer from RSI symptoms“
The wrist area is “the most common RSI trouble spot: A survey on RSI trouble spots found that wrist pain is the most common point of pain out of all RSI related injuries “:

“Up to 23.8% more women complain of RSI symptoms compared to men: More women have poor office health compared to men. A workforce survey by the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health found that 63.5% of women experience neck and shoulder pain while only 39.7% of men do. The same goes for back pain, which is more common in women (51.4%) than men (44%). “
” 33% of workers with RSI are below 45 years old: Surprisingly, about one-third of workers with RSI are under 45. [9] This number is quite high considering the fact that degeneration due to old age is still not yet a factor at that point.”
” 62.2% of young workers do repetitive motions at least 25% of their work time: Based on the European Survey on Working Conditions 2000 report, a majority of workers aged 15 to 24 years old are exposed to repetitive motions for at least a quarter of their work time. This can lay the foundation for developing RSI later in life.”
“34% of all lost workdays are due to work-related musculoskeletal disorders: The data collected by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) indicates that work-related RSI’s are the most common reason for lost or restricted work time, accounting for more than a third of lost workdays. “
“Most injuries take an average of 9 days for full recovery while RSI’s require 23 days off work on average.”
Resources
Jon MullerI’m a mechanical engineer and founder of ErgonomicTrends.com. Good Form. Good Function. Good Health. (2020, October 12). 42 New Statistics on RSI and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Every Worker Should Know. Retrieved October 20, 2020, from http://ergonomictrends.com/rsi-statistics/

“A repetitive strain injury (RSI), sometimes referred to as repetitive stress injury, is a gradual buildup of damage to muscles, tendons, and nerves from repetitive motions. RSIs are common and may be caused by many different types of activities, including:
Some common RSIs are:
“
Resources
Hecht, M. (2017, March 14). Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI): Causes, Prevention, and More. Retrieved October 20, 2020, from https://www.healthline.com/health/repetitive-strain-injury
The “creative industry” also called the “creative and digital industries” is defined as “a range of economic activities that are concerned with the generation and commercialization of creativity, ideas, knowledge and information.”
The creative industry is said to include sectors like “design, music, publishing, architecture, film and video, crafts, visual arts, fashion, TV and radio, advertising, literature, computer games and the performing arts.”
Sources
Parrish, D. (2019, December 19). Creative Industries definitions. Retrieved October 18, 2020, from https://www.davidparrish.com/creative-industries-definitions/
© 2024 A better way to control your computer
Theme by Anders Noren — Up ↑